Diabetes
What Are Diabetes?
Diabetes represents a long-term disease which disrupts the body’s blood sugar (glucose) level management system. Every body cell uses glucose as its primary energy source which the pancreas regulates by producing insulin. Diabetes results in interrupted glucose regulation which causes blood sugar levels to become higher than normal through the medical condition called hyperglycemia. Unmanaged diabetes produces life-threatening problems that harm major organs including the heart and kidneys along with eyes and nerve tissues
Types of Diabets
There are three main types of diabets: Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabets.
- Type 1 Diabetes
An autoimmune disorder known as type 1 diabetes leads the immune system to destroy beta cells in the pancreas that produce insulin mistakenly. Therefore insulin production within the body becomes negligible or stops altogether. Young adults and adolescents are most often first diagnosed with this type of diabetes although anyone from made flavor allowed can have it develop. People who have Type 1 diabetes need insulin injections every day or the continuous supply from an insulin pump to control their blood sugar levels. - Type 2 Diabetes
The majority of diabetes cases in the population involve Type 2 diabetes which represents between 90 and 95 percent of all known diabetes cases. The condition happens because the body shows resistance to insulin effects or due to insufficient insulin production by the pancreas. Type 2 diabetes develops through lifestyle factors like poor diet choices and physical inactivity and obesity but genetic predisposition affects patients as well. Type 2 diabetes remains more prevalent among adults but pediatric endocrinologists are discovering it in children and adolescents at greater rates because childhood obesity continues to climb. - Gestational Diabetes
During pregnancy women develop gestational diabetes but the condition generally goes away after delivery. Development of Type 2 diabetes becomes more likely later for both mother and child when gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy. Pregnancy hormone variations create insulin usage problems in the body leading to this specific diabetes type.
Symptoms of Diabetes
Diabetes symptoms change according to both the condition type and its severity. Common symptoms include:
Frequent urination
Excessive thirst
Extreme hunger
Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
Blurred vision
Slow-healing wounds
Tingling and numbness shows up specifically in hands and feet when a person has Type 2 diabetes.
Seek medical advice if you notice these symptoms continue to appear.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact causes of diabetes depend on its type:
Type 1 Diabetes:An autoimmune process causes the condition yet medical professionals do not yet understand the triggering process which might involve both genetic and environmental aspects.
Type 2 diabetes:Lifestyle factors model along with obesity, genetic family patterns and advanced age determine Type 2 diabetes causes.
- **Gestational diabetes:Hormonal shifts during pregnancy create gestational diabetes and prior obesity along with previous gestational diabetes history increase chances of its development.
Managing Diabetes
Effective diabetes management focuses on maintaining healthy blood sugar levels through a combination of:
Medication:Patients who need to manage blood sugar levels use insulin together with prescribed oral medications.
Diet:Maintain good health with nutritious whole grain and vegetable meals while choosing lean proteins and restricting both added sugar and harmful fats.
Exercise:Exercising regularly will help boost the body’s insulin sensitivity.
Monitoring:People should routinely conduct blood sugar tests to keep track of level patterns.
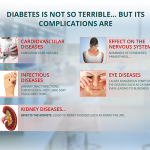
Complications of Diabetes
Unmanaged diabetes produces severe health problems which include cardiovascular disease and kidney failure alongside eye conditions (diabetic retinopathy) nerve damage (neuropathy) and higher susceptibility to infections. The successful prevention of long-term complications from diabetes requires early diagnosis combined with appropriate medical management.
Although diabetes presents its challenges recognized through its complexity this condition generally can be controlled effectively. People with diabetes achieve healthy life experiences by managing their condition through proper education and medical treatments together with lifestyle modifications.

Why Is That?
The body’s process of converting blood sugar (glucose) into essential cellular energy is disrupted by diabetes which persists as a chronic health condition. The dramatic rise in diabetes cases through the past few decades has become a public concern and triggered an urgent examination of its etiological factors. So, why does diabetes occur? Diabetes develops through a complicated network between genetic components and environmental plus lifestyle choices.
Types of Diabetes
Diabetes primarily manifests in three forms: Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes. Each type has distinct causes and risk factors:
- **Type 1 diabetes:
A specialized autoimmune disease known as Type 1 diabetes most frequently appears among children and young adults. In this condition the body’s immune system targets and destroys the beta cells which produce insulin in the pancreas. The body fails to maintain glucose level control when insulin production stops. Although researchers do not fully understand Type 1 diabetes origins environmental factors together with genetic susceptibility appear to play major roles in its development. - **Type 2 diabetes:
The prevalence of this diabetic disorder makes it the leading type associated with both lifestyle habits and advancing years. People with type 2 diabetes experience insulin resistance alongside decreased insulin production because their pancreas cannot maintain usual glucose levels. Risk factors for diabetes emerge from obesity and physical inactivity besides high-calorie eating habits combined with genetic susceptibility. Because this type of diabetes progresses little by little researchers show how vital it is to prevent it early. - **Gestational Diabetes:
Hormonal alterations during pregnancy produce gestational diabetes by disturbing normal insulin operation. Typically childbirth ends this condition but it creates future Type 2 diabetes risks for both mother and child.
Why Does Diabetes Develop?
The body develops diabetes when it loses control over glucose and insulin regulation. Here’s a deeper look at contributing factors:
- **Genetics:
Personal medical background remains one of the main determinants of diabetes risk. Research shows special genes affect pancreatic function and the way all bodily tissues react to insulin. Having a parent or sibling who has diabetes increases the chance you will develop this disease in your lifetime and you have a higher probability of getting Type 2. - **Lifestyle Choices:
Diabetes prevention must address both inactive lifestyles and unhealthy food patterns because they directly lead to disease progression. A meal plan high in processed sugars and unhealthy fats while low in fiber contributes to unnecessary weight gain and insulin resistance in individuals. A lack of physical activity worsens these problems because it hampers proper glucose usage by the body. - **Obesity:
Having extra weight principally around one’s middle reaches directly toward insulin resistance. Inflammatory molecules produced by fat cells disrupt the function of insulin when it regulates blood sugar levels. - **Environmental and socioeconomic factors:
The interaction between urban areas creation alongside restricted healthy food availability and intense stress environments leads to higher chances of developing diabetes. Financial and social disadvantages limit people’s ability to keep their health and fitness as top priorities. - **Age and hormonal changes:
As people grow older they face a higher chance of developing type 2 diabetes because their metabolic systems evolve and physical activity decreases along with hormonal alterations. - **Medical conditions and medications:
Certain medical conditions and some medications create problems with glucose processing leading to elevated diabetes rates.
Preventing Diabetes
No matter the unchangeable nature of genetics people possess the ability to lower diabetes risk through lifestyle changes. You can prevent diabetes effectively through regular physical activity alongside balanced nutrition and healthy weight management while also managing stress levels. Routine health assessments provide early diagnosis of diabetes or prediabetes so that immediate intervention measures can begin.
Conclusion
Combating diabetes’ growing rates depends upon understanding the disease. Through root cause intervention and proactive measures people can minimize their future health risks while achieving better wellness. The combined power of education along with early intervention measures and lifestyle modifications offers the primary solution to control the global health challenge we face.
How to Avoid It
A widespread chronic medical condition exists that affects millions throughout the world in different regions. A lack of proper blood sugar management leads to this health condition. There are two primary types of diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 diabetes develops because of genetic causes making prevention minimal, but interventions through lifestyle changes can prevent many cases of Type 2 diabetes. Improved health practices help decrease your risk of diabetes while simultaneously boosting your general health.
Understand the Risk Factors
People who learn about the factors causing diabetes stand a better chance of preventing the disease. Obesity and physical inactivity together with unhealthy eating practices plus genetic predispositions stand as the main risk elements which may lead to Type 2 diabetes. Age and ethnicity together with specific medical conditions (including polycystic ovary syndrome) represent other important factors that boost your risk.
Awareness of your personal diabetes risk enables you to take necessary actions that counteract contributing factors. People with diabetes in their family tree can greatly reduce their risk of developing the disease through effective lifestyle adjustments.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Abdominal obesity produces insulin resistance that acts as a defining characteristic of type 2 diabetes. Staying within a healthy body weight range stands out as the best strategy for preventing the condition.
Make physical exercise and balanced nutrition fundamental parts of your routine with whole foods and fruits and vegetables and proper sources of protein and fats. The combination of extreme dieting strategies or radical calorie cuts leads to persistent metabolic problems. Work toward slow weight loss which you can maintain over time.
Exercise Regularly
The body’s insulin efficiency improves through physical exercise establishing regular blood sugar levels. According to the World Health Organization people should perform no less than 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise during every seven days. People should choose brisk walking or cycling and swimming as alternative fitness options because these activities provide several health benefits.
Strength training is equally important. Muscle building enhances glucose management for your body which lowers diabetes possibility. Strength exercises along with aerobic workouts bring your best fitness results.
Adopt a Balanced Diet
Eating properly remains crucial when trying to prevent diabetes. To prevent diabetes eat different nutritious foods while you cut back on processed meals refined carbs and sugary snacks.
**Key dietary tips include:
- Choose whole grains: Replace white bread, pasta, and rice with whole-grain alternatives like quinoa, brown rice, and whole-wheat bread.
Limit sugar intake:Avoid sugary drinks together with desserts and snacks. Select natural sweetener choices or benefit from fruits which already have their own natural sweetness.
Embrace healthy fats:** Incorporate sources of healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, into your diet.
Prioritize fiber-rich foods:Legumes and whole vegetables along with whole fruits provide enough fiber to extend glucose release into the bloodstream which helps maintain stable sugar concentrations.
Manage Stress
Bodywide tension mounted from long-term stress raises blood sugar levels and leads people toward unhealthy behaviors like overeating and remaining inactive. Use relaxation methods that include trying meditation along with yoga exercises deep breathing practices and involving yourself in favorite pastimes.
Get Regular Health Check-Ups
Regular medical assessments serve to identify early detection markers for diabetes which encompass prediabetes. Medical teams can intervene early to stop the progress toward complete diabetes development. Have conversations with your physician about risks that affect you combined with regular blood sugar screening when appropriate.
Prioritize Sleep
Both inadequate sleep duration and poor-quality sleep can lead to insulin dysregulation which increases diabetes risk. To obtain 7–9 hours of quality sleep every night connect to a regular sleep pattern while making your sleeping surroundings comfortable and silent.
Conclusion
A healthy lifestyle needs commitment for diabetes prevention. A balanced diet combined with regular physical activity and dedication to stress management and adequate sleep serves to significantly lower the risk you face. Persistent minor adjustments to lifestyle habits together can help us achieve better overall health outcomes.

What is the doctor’s advice?
Diabetes represents a persistent health problem which impacts the mechanism by which the human body processes its blood sugar content known as glucose. A person develops diabetes when their pancreas fails to produce sufficient insulin or their body remains unable to use the insulin it produces. To prevent complications in heart disease and other damaging conditions physicians emphasize critical management of diabetes. Doctors help their patients by providing vital guidance toward proper diabetes management which enables healthier living. The standard guidance doctors offer people diagnosed with diabetes unfolds as follows.
1. Understand Your Type of Diabetes
There are three main types of diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes: the body develops an autoimmune reaction that destroys cells which produce insulin. Type 2 diabetes: Most common among diabetes types Type 2 is linked to insulin resistance because of lifestyle behaviors such as obesity combined with physical inactivity.
Gestational diabetes**: A diabetes condition which emerges from pregnancy typically disappears post childbirth.
Your healthcare professional will determine your diabetes type to create personalized recommendations.
2. Adopt a Healthy Diet
Changing what you eat represents a critical component of effective diabetes management. Doctors typically recommend:
Low-glycemic foods: When diet prioritizes whole grains mixed with vegetables and legumes along with lean proteins people can achieve stable blood sugar levels. Portion control: By eating multiple small meals throughout the day you can keep your blood sugar from surging.
Minimize sugary and processed foods**: Cut down consumption of sweet drinks along with candies and processed sugar byproducts.
By working with a dietitian it’s possible to develop a specialized eating plan.
3. Incorporate Regular Exercise
Exercise makes the body process insulin more effectively. Doctors recommend that adults complete at least 150 minutes of moderate intensity physical activity such as brisk walking along with cycling and swimming each week. Lifting weights as part of resistance training programs will help regulate blood sugar. Diabetic patients need to check their blood sugar levels prior to exercising and again afterwards to prevent hypoglycemia.
4. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
Blood glucose level monitoring maintains essential health management. Your doctor may recommend:
Anyone with diabetes should maintain regular glucose checks by employing both glusern Fusion
Gain knowledge about the effects of nutritional choices together with physical activity and medication use on your blood sugar readings.
Users need to record their results as they look for patterns and identify which adjustments they need to apply.
5. Take Prescribed Medications
Depending on your diabetes type, your doctor may prescribe:
Insulin therapy: essential for Type 1 diabetes and sometimes for advanced Type 2. Oral medications: Type 2 diabetes often requires oral drugs including metformin because of its ability to increase insulin sensitivity.
Your optimal blood sugar levels require strict adherence to prescribed medication dosage and timing
6. Prevent and Manage Complications
Medical professionals insist on preventive actions in order to protect against disease complications.
Regular check-ups: Patients need to check their kidney function together with both cholesterol levels and blood pressure in routine assessments. Foot care: Patients need to perform routine inspections of their feet for any signs of sore or infection presence.
Eye exams**: Identify diabetic retinopathy symptoms early and take steps to control them immediately.
7. Stay Educated and Seek Support
Establishing continuous monitoring throughout life is required because diabetes persists as a long-term illness. Health professionals advise patients to keep current on medical advancements for better disease treatment. Both peer support programs and diabetes expert guidance deliver useful educational opportunities with added support mechanisms.
Conclusion
Successful diabetes control requires both medical instructions and patients to change their lifestyle while actively managing their health routine by themselves. People with diabetes who stick to their doctor’s instructions achieve improved blood sugar management and experience fewer health problems along with better overall life quality.
How many years have we dealt with this condition?
This chronic disease which triggers high blood glucose dates back thousands of years into human history. Medical documentation on this disease exists from antiquity onwards though modern knowledge about it has advanced greatly. Let’s trace diabetes through time from its primary mentions until the achievement of modern wellbeing solutions.
Ancient Observations
Health practitioners from ancient civilizations documented diabetes several thousands of years ago. Diabetes appeared for the first time in medical writings from historical Egyptian and Indian sources around the year 1500 BCE. The ancient Egyptian medical Ebers Papyrus documented symptoms akin to diabetes that included repeated urination together with extreme thirst. Indian physicians of that period called diabetes “Madhumeha” meaning “honey urine” because affected patients had sweet-smelling and tasting urine which eventually helped diagnose the condition.
The word “diabetes” came into existence from Greek doctor Aretaeus of Cappadocia during the 1st century CE. The physician Aretaeus called the disease “a decomposition of body tissues into urine.” Even with early medical observations people remained unable to understand diabetes treatment until recent history.
Advances in the Middle Ages
Both Eastern and Western medical practice during the Middle Ages recognized diabetes as a disease. The Canon of Medicine by Avicenna covered signs such as abnormal appetite together with disease progression which established foundations for future scientific investigations.
From a European perspective diabetes presented as a sporadic illness that medical practitioners misunderstood during historic times. Before modern medical science developed, physicians explained the condition as a consequence of imbalance in the four bodily fluids of humoral theory.
The Renaissance and Beyond
During the Renaissance period scientists and doctors intensified their study of human anatomy alongside general scientific inquiry. Thomas Willis joined “mellitus” to diabetes during the 17th century because he wanted to describe urine’s sweetness. Thomas Willis identified sugar content in patient urine as the main difference between diabetes and different diseases that produce frequent urination.
During the late 1700s medical scientists recognized a connection between diabetes and the pancreas. Paul Langerhans discovered pancreatic clusters of cells in 1869 which would come to be called islets of Lanagerhans before scientists identified them as insulin-producing structures.
The Discovery of Insulin
During the 20th century researchers achieved essential breakthroughs in the field of diabetes study. The scientists Frederick Banting—who worked alongside Charles Best in Canada—made the discovery of insulin from canine pancreases during 1921. The discovery that changed diabetes care gave people suffering from type 1 diabetes access to life-saving treatment. Banting earned the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1923 because of his discovery of insulin’s medical significance.
Modern Perspectives
Diabetes remains a worldwide health emergency by affecting more than 537 million individuals today. Type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes form three separate categories because they originate from different causes that require specialized treatments. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) together with insulin pumps represent technological progress that has optimized management and future stems from research on artificial pancreas systems and stem cell therapies.
Looking Ahead
Medical progress has not eliminated all difficulties associated with diabetes. Higher obesity rates along with increased sedentary lifestyles support the rapid growth of type 2 diabetes prevalence. This developing epidemic requires public health programs that support lifestyle adjustments and promote both timely identification and equal medical care access to prevent and manage its reach.
What began as an ancient condition continues to reveal human persistence along with scientific breakthroughs through its timeline of diabetes research and treatment development. Although treatment advances remain crucial the development of diabetes therapies continues as researchers search for a definitive cure.
What Is the Way to Survive?
The chronic disease diabetes disrupts how the body uses blood sugar or glucose which functions as a fundamental energy source. There are three main types of diabetes: Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes. All diabetes types require the patient to manage blood sugar levels to prevent serious health issue development even though their origin and therapy methods differ. A multidimensional approach which combines learner education with lifestyle modifications and regular medical care enables patients to survive and flourish with diabetes.
Understanding the Basics
The autoimmune condition known as Type 1 diabetes destroys insulin-producing pancreatic cells through attacks by the body’s immune system. Because their pancreases destroy their insulin-producing cells the patients who develop type 1 diabetes need to use daily insulin injections or operate insulin pumps to survive. In contrast to Type 1 diabetes Type 2 diabetes affects more people because it mainly develops from unhealthy eating habits along with obesity and insufficient exercise. Type 2 diabetes develops because the body stops responding properly to insulin alongside inadequate insulin production. Diabetes develops during pregnancy but goes away post-childbirth yet it boosts lifetime risk factors for TYPE 2 diabetes.
Diabetes serves as more than a medical disorder because it transforms the entire way people live their lives. Failure to manage the condition will result in major health problems like heart disease along with kidney failure and nerve damage which cause vision loss. People with diabetes have achievable survival options once they implement proactive discipline into their treatment regimen.
The Pillars of Survival
- Education and Awareness
Effective diabetes management depends on gaining proper understanding of the disease. Managing diabetes effectively covers food effect studies on blood sugar levels while identifying both high and low blood sugar symptoms and understanding needed medications. Diabetes education and support programs offer critical knowledge together with emotional backing systems. - Healthy Eating
Blood sugar management depends heavily on proper nutritional choices for people living with diabetes. The toxins from whole grains alongside lean protein sources healthy fats and abundant fruits and vegetables produce balanced nutrition which sustains blood sugar levels. People with diabetes need strict portion control while monitoring their carbohydrate consumption because carbohydrates primarily affect blood glucose levels. Development of personalized meal plans becomes easy through consultations with registered dietitians who specialize in dietary needs. - Regular Physical Activity
Physical exercise enhances how well your body uses insulin to absorb glucose. Walking through strength training sessions or cycling along with swimming yields positive health benefits. Individuals should reach and maintain 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity every week. A consultation with a healthcare provider must happen before beginning any new exercise program when diabetes-related complications exist. - Medication and Monitoring
Following your healthcare provider’s medication prescriptions including insulin and oral diabetic drugs persists as essential for effective diabetes management. Consistent blood glucose measurements enable recognition of patterns that limit dangerous high and low blood sugar events. Continuous glucose monitors along with insulin pumps work together to deliver precise control of diabetes management. - Stress Management
The continuous presence of stress causes dysfunction in blood sugar regulation. Mindfulness methods together with yoga practice and deep breathing serve to control stress levels. Having family and friends as part of your support network helps lift emotional stress. - Regular Checkups
Early detection of medical problems requires patients to participate in routine medical checkups. Good medical practice requires regular evaluations of patients’ blood pressure and cholesterol along with kidney and eye health checks.
Thriving with Diabetes
Managing diabetes involves surpassing simple preventative measures to achieve a full and rewarding existence despite the disease. The required major changes lead to superior health outcomes. Through consistent care and positive thinking people living with diabetes have the potential to enjoy fulfilling lives that last. Survival is just one part of life with diabetes because true success lies in creating a vibrant life experience.